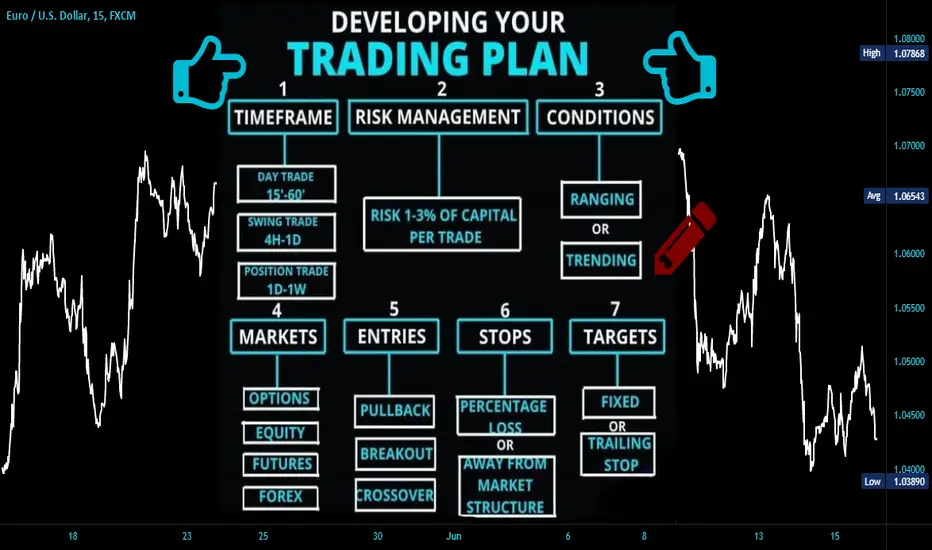
In the fast-moving world of forex trading, prices can change in the blink of an eye. One moment, you’re in profit — the next, a sudden market move wipes out your gains. That’s why smart traders don’t just focus on making profits — they focus on protecting them.
This is where hedging comes in.
Hedging is like having an insurance policy for your trades. It won’t always increase your profits, but it can help you reduce losses and keep your capital safe when the market turns against you.
Let’s dive into what hedging means, how it works in forex, and the different strategies you can use to protect your money while still staying in the game.
💡 1. What Is Hedging in Forex?
In simple terms, hedging means opening a position — or a series of positions — to offset potential losses from another trade.
It’s a risk management technique that helps you protect your portfolio when the market moves unexpectedly.
Think of it like this:
If you own a car, you buy insurance to protect yourself from accidents.
If you trade forex, you hedge your positions to protect yourself from market “accidents.”
Hedging doesn’t eliminate risk entirely — but it can reduce it significantly.
🔁 2. How Does Hedging Work in Forex Trading?
Forex trading always involves currency pairs — one currency is bought, and the other is sold.
When you hedge, you open a new position that moves in the opposite direction of your existing trade. This way, if one trade loses money, the other gains — helping you balance the impact.
Example:
Let’s say you bought EUR/USD at 1.1000 because you expect it to rise.
But you’re worried about short-term volatility.
To protect yourself, you open a sell trade (short) on EUR/USD at the same time.
If the price drops, your long position loses — but your short position gains.
If the price rises, your short position loses — but your long position gains.
In both cases, your losses are limited — that’s the power of hedging.
⚙️ 3. The Main Types of Forex Hedging
There’s more than one way to hedge your forex positions. Let’s explore the most popular methods used by traders worldwide.
🔄 A. Direct Hedging
This is the simplest and most common type of hedge.
You open two opposite trades on the same currency pair — one buy and one sell.
For example:
- You’re long (buying) GBP/USD at 1.2500
- You open a short (sell) position on GBP/USD at 1.2550
The idea is to hold both positions until the market gives you a clearer direction.
Even if the price fluctuates wildly, your overall exposure is reduced.
Pros:
- Easy to understand and execute
- Offers immediate protection from short-term volatility
Cons:
- You might pay double spreads or swap fees
- Profit potential becomes limited while both trades are open
🔀 B. Cross-Currency Hedging
Instead of opening opposite trades on the same pair, you can hedge using related currency pairs.
For example:
If you have a long position on EUR/USD, you might open a short on GBP/USD.
Because both pairs include the U.S. dollar, they tend to move in similar directions — but not always perfectly.
This kind of hedge gives you flexibility, but it also requires a good understanding of currency correlations.
Pros:
- More dynamic and flexible
- Can be used to protect positions indirectly
Cons:
- Correlations can change over time
- Harder to calculate exact protection levels
📊 C. Using Options for Hedging
Currency options are powerful tools for advanced traders.
A forex option gives you the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a currency at a specific price before a certain date.
For example:
If you’re holding a long position on EUR/USD, you can buy a put option (the right to sell) to protect against a fall in price.
If the market drops, your option increases in value — offsetting the losses on your main trade.
Pros:
- Protects against downside risk while keeping upside potential
- Flexible and professional hedging tool
Cons:
- Options have a cost (called a “premium”)
- More complex than standard spot trading
💹 D. Using Futures or Forward Contracts
Institutional traders or large investors sometimes use currency futures or forwards to hedge.
These are agreements to buy or sell a currency at a future date and a fixed rate.
They’re excellent for businesses or investors who want to lock in an exchange rate to avoid future price fluctuations.
However, they’re less common for retail traders because they require larger contracts and more capital.
🧠 4. Why Forex Traders Use Hedging
Hedging isn’t about avoiding risk completely — it’s about managing it.
Here are the main reasons traders use hedging strategies:
- To protect profits from an existing position
- To reduce losses during uncertain market conditions
- To stay active in the market without closing positions
- To manage news events like central bank meetings or economic releases
In short, hedging helps traders stay calm and in control — even when the market gets wild.
⚠️ 5. The Risks and Limitations of Hedging
While hedging can be helpful, it’s not a magic shield. Here are a few important things to keep in mind:
- Reduced Profit Potential: When one trade gains, the other usually loses — limiting overall profit.
- Extra Costs: You might pay more in spreads, swaps, or premiums (for options).
- Complexity: Advanced hedging strategies require solid market knowledge.
- Timing: Poor timing can turn a protective hedge into an unnecessary loss.
Remember: The goal of hedging isn’t to win more — it’s to lose less.
🧭 6. When Should You Use Hedging?
Not every situation calls for hedging. It’s best used when:
- You expect short-term volatility but believe in your long-term position.
- You’re trading around major news events or rate decisions.
- You have multiple open positions in correlated pairs.
If the market looks uncertain and you don’t want to close your main trade, a hedge can buy you time — and peace of mind.
💬 7. Tips for Effective Hedging
Want to hedge like a pro? Follow these smart tips:
- Have a Clear Plan: Know when to open and close your hedge.
- Avoid Over-Hedging: Too many opposite trades can cancel out your profits.
- Understand Correlations: Learn how currency pairs move together.
- Keep Costs in Mind: Don’t let spreads or swap fees eat your returns.
- Practice First: Try hedging on a demo account before risking real money.
✅ Final Thoughts: Hedge Smart, Trade Confidently
Hedging is one of the most powerful risk management tools in the forex world.
It’s not about predicting every market move — it’s about being prepared for whatever happens next.
By learning how to hedge effectively, you can protect your profits, reduce stress, and trade with confidence — no matter how unpredictable the market becomes.
So remember:
“Great traders don’t just make profits — they protect them.”
Trade smart, manage your risk, and let hedging be your invisible shield in the forex battlefield.